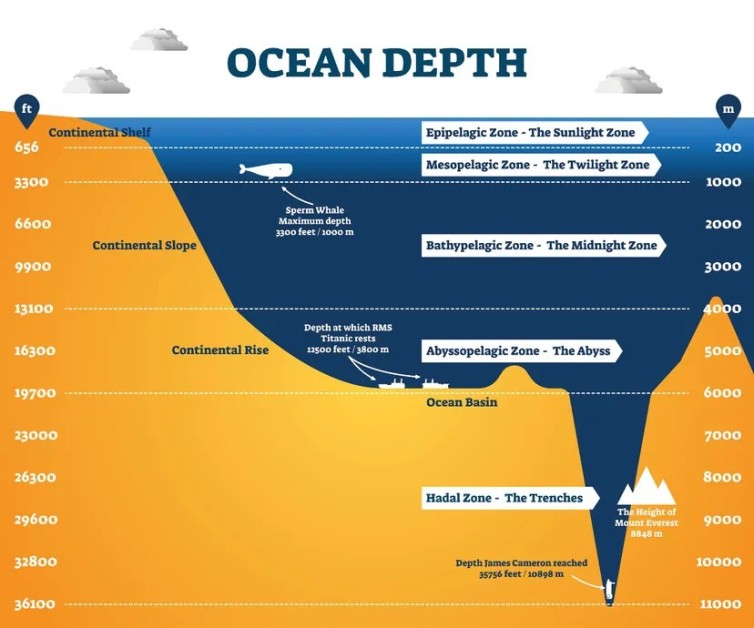
Earth’s staggering depth, explained
The depths of the ocean have always fascinated humanity. From the surface, the sea appears as a vast expanse of water, but beneath its shimmering surface lies a realm of mystery and wonder. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the enigmatic world of the ocean’s depths, exploring the various layers and zones that make up this hidden universe. From the sunlit shallows to the pitch-black abyss, we will uncover the secrets of the deep sea.
Exploring the Abyss: An Overview
The exploration of the ocean’s depths has been a challenging endeavor for scientists and adventurers alike. The ocean covers more than 70% of the Earth’s surface, making it a critical part of our planet’s ecosystem. To understand and protect this vast environment, we must first answer a fundamental question: How deep is the ocean?
Defining Ocean Depth
Ocean depth is not a straightforward concept. It varies across different parts of the world’s oceans and is affected by various factors such as tides, currents, and underwater terrain. To accurately measure the depth of the ocean, scientists use advanced equipment and technology that allows them to map the seafloor and explore the mysteries of the deep.
The Epipelagic Zone
Sunlight Penetration
The epipelagic zone, also known as the sunlight zone, is the uppermost layer of the ocean. It extends from the surface to a depth of about 200 meters (656 feet). In this zone, sunlight penetrates, allowing photosynthesis to occur. This light sustains a diverse range of marine life, including phytoplankton, zooplankton, and various fish species.
Depth Range
The epipelagic zone is relatively shallow compared to the rest of the ocean, but it plays a crucial role in supporting marine ecosystems. It is the warmest layer of the ocean and experiences the most significant temperature fluctuations throughout the day.
Marine Life in the Epipelagic Zone
The sunlight zone teems with life. It is home to a wide variety of fish, including popular species like tuna and swordfish. Additionally, countless species of smaller fish and invertebrates inhabit this zone, forming the base of the oceanic food chain.
The Mesopelagic Zone
Twilight Zone
Descending below the epipelagic zone, we enter the mesopelagic zone, often referred to as the twilight zone. This zone extends from depths of around 200 meters to 1,000 meters (656 to 3,280 feet). Here, sunlight becomes progressively dimmer, casting an eerie twilight-like ambiance.
Depth and Characteristics
The mesopelagic zone is characterized by a unique set of environmental conditions. The water is cold and dark, and the pressure increases significantly as we venture deeper. These conditions present challenges for both organisms and researchers exploring this mysterious realm.
Mysterious Creatures of the Mesopelagic Zone
Despite the challenging conditions, the mesopelagic zone is not devoid of life. In fact, it is home to an array of fascinating and often bizarre creatures. From bioluminescent jellyfish to elusive lanternfish, the twilight zone harbors a rich and poorly understood ecosystem.
The Bathypelagic Zone
Midnight Zone
Descending further into the ocean, we enter the bathypelagic zone, also known as the midnight zone. This zone begins around 1,000 meters (3,280 feet) below the surface and extends to depths of about 4,000 meters (13,123 feet). In the bathypelagic zone, sunlight is entirely absent, plunging the environment into perpetual darkness.
Depth and Conditions
The bathypelagic zone is a realm of extreme pressure and near-freezing temperatures. The immense weight of the water above exerts tremendous pressure on any organisms that call this zone home. Survival here requires specialized adaptations to withstand the harsh conditions.
Adaptations of Deep-sea Life
Life in the bathypelagic zone has evolved in remarkable ways. Some species have developed bioluminescent organs to navigate and communicate in the dark. Others have elongated bodies and expandable stomachs to conserve energy and capture prey efficiently. These adaptations are a testament to the resilience of life in the deep sea.
The Abyssopelagic Zone
Abyssal Zone
Descending even deeper, we reach the abyssopelagic zone, commonly referred to as the abyss. This zone starts at around 4,000 meters (13,123 feet) and extends to depths of approximately 6,000 meters (19,685 feet). The term “abyss” aptly describes the profound depths of this zone.
Unimaginable Depths
The abyssal zone is one of the least explored regions on Earth. Its immense pressure, frigid temperatures, and inky darkness make it a formidable challenge for scientists and researchers. Yet, this mysterious realm holds untold secrets waiting to be uncovered.
Bizarre Creatures in the Abyss
Life in the abyssal zone is nothing short of astonishing. From giant squid with enormous eyes to deep